Accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment for a commonly overlooked source of pain
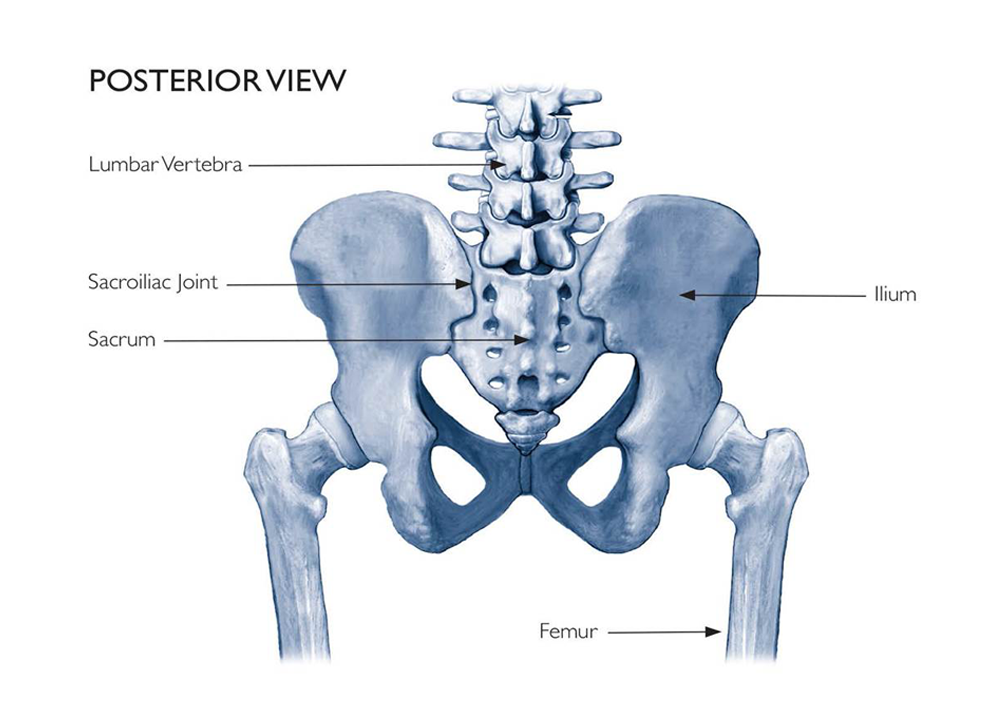
Sacroiliac (SI) joint dysfunction is a frequent but often underdiagnosed cause of lower back, buttock, and hip pain. Because its symptoms can closely mimic disc or nerve-related conditions, precise evaluation is essential.
At Virginia Spine Specialists, we use a careful, evidence-based approach to identify SI joint pain and deliver effective treatment—starting with conservative care and advancing to minimally invasive options when appropriate.
Understanding the Sacroiliac ( SI ) Joint
The pelvis is the largest bony part of the skeleton and contains three joints: the pubic symphysis and two sacroiliac joints. The sacroiliac joints connect the sacrum (base of the spine) to the pelvis, playing a critical role in transferring forces between the upper body and legs.
The sacroiliac ( SI ) joints are strong, weight-bearing synovial jonts. They connect the base of the spine (sacrum ) to the iliac bones on either side of the pelvis. This connection, made through mutliple strong ligaments and muscle, transfers the weight from the upper body down to the legs.
The SI Joint is a viscoelastic joint and is not designed for a large amount of motion. The primary purpose for the SI joint is to provide shock absorption and to reduce the amount of stress exerted on the spine.
- A highly durable network of ligaments surrounds the sacroiliac joints giving them tremendous strength.
- Minimal movement in Sacroiliac joints ( only 2 – 4 mm ).
- More movement in women to allow for childbirth.
- The SI joint provides shock absorption and reduces the amount of stress exerted on the spine
Although the SI joint allows only limited movement, even small disruptions in stability or inflammation can cause significant pain.
Diagnosing SI Joint Pain
Sacroiliac ( SI ) Joint Pain is a challenging condition that affects 15 – 25% of patients with low back pain.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of pain in the SI joint include:
- Low back pain
- Pelvis/buttock pain
- Lower extremity pain
- Hip/groin pain
- Problems sitting, sleeping, or walking
Common Causes
SI joint dysfunction may result from:
- Inflammation or arthritis of the joint
- Injury or trauma (falls, accidents)
- Pregnancy or postpartum changes
- Leg length differences or altered gait
- Prior lumbar spine surgery
SI joint degeneration occurred 75% of the time in patients undergoing lumbar fusion at 5 years post-surgery.
Treatment Options
Conservative (Non-Surgical) Treatment
There are a number of treatment options for patients who suffer from the symptoms associated with sacroiliac joint problems. Conservative methods are typically recommended first and may include:
- Physical therapy focused on pelvic and core stabilization
- Anti-inflammatory medications
- Image-guided SI joint injections to reduce inflammation and confirm diagnosis
- Activity modification and supportive bracing (sacroiliac belts), when appropriate
These treatments aim to relieve pain while allowing the disc and surrounding tissues to heal.
Additionally, oral medications may be used as well as therapeutic injections that my provide some patients a temporary relief of pain. Radiofrequency ablation techniques may be suggested but similar to injections may only provide temporary relief.
Minimally Invasive Surgical Treatment
Surgical intervention may be considered after non-surgical interventions have failed to provide a significant amount of patient symptom relief. Minimally invasive SI joint stabilization or fusion may be considered in select patients. Sacroiliac joint fusion provides stabilization of the joint and eliminates motion in the joint, typically providing long-term pain relief for patients.
These procedures:
- Use small incisions
- Minimize disruption to surrounding tissue
- Aim to stabilize the joint and reduce painful motion
- Often allow faster recovery than traditional open surgery
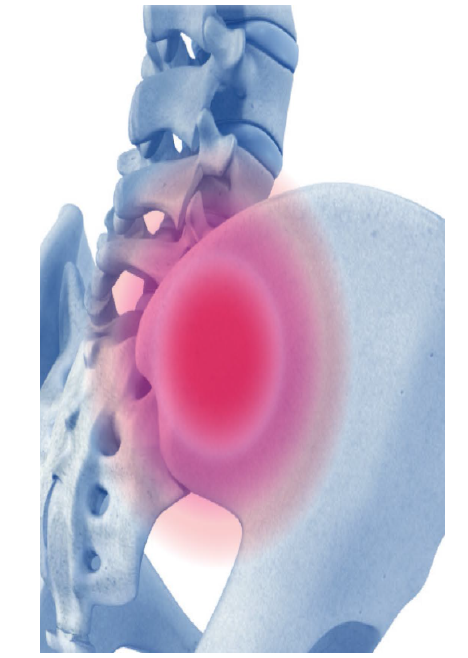
The SI JOIN™ Procedure
The SI Join™ Sacroiliac Joint Fusion System consists of three Allograft (Bone) implants placed at opposing angles to increase SI Joint stability. The procedure is performed through a posterior approach, decreasing the chance for possible neural complications as associated with lateral approaches. The procedure is performed through three small incisions in the lower back, resulting in lower surgical trauma, reduced blood loss, shorter surgery times, and faster recovery.
SI Join™ Procedural Advantages
- SI joint procedures have been performed since the 1920’s with positive results, SI Join™ is an advancement on this proven procedure.
- Less procedural blood loss and less post-operative pain than in order sacroiliac fusion procedures, resulting in faster recovery times.
- Small in size when compared to other surgical options, while still having comparable strength due to the implant’s patented design.
- Eliminates the need for bulky metal hardware to achieve stabilization and fusion of the SI Joint.
- Less traumatic than lateral screw and rod based systems.
- Joint preparation combined with the allograft (bone) implants enhances fusion across the SI Joint.
Contraindications and Warnings
Contraindications for the SI Join™ – Direct Posterior Fusion system include, but are not limited to the following:
- Infection
- Deformity that would affect the placement of the SI Join™ implants.
- Tumor resection
- Gross joint instability of dislocation
There are associated risks and recovery times with any surgical procedure. Please consult Dr. Sharma for a complete list of contraindications, warnings, post-operative guidelines, and other precautions associated with this procedure.
When to Seek Expert Evaluation
Consider specialist evaluation if:
- Lower back or buttock pain persists despite treatment
- Pain interferes with walking, standing, or daily activities
- Symptoms return after spine surgery
- Imaging does not fully explain ongoing pain
Accurate diagnosis is key to avoiding unnecessary or ineffective treatments.
Expert Spine Care with Dr. Mudit Sharma
Dr. Sharma is a board-certified neurosurgeon with extensive experience diagnosing and treating SI joint dysfunction using modern, minimally invasive spine and joint techniques.
At Virginia Spine Specialists, you’ll receive:
- Personalized treatment plans
- Access to advanced minimally invasive techniques
- Compassionate, patient-centered care close to home
Call (571) 921-4877 for an appointment.
Serving the residents of Prince William, Spotsylvania, and Loudoun counties in Northern Virginia
Frequently Asked Questions
Diagnosis involves a detailed physical exam, imaging studies, and often image-guided diagnostic injections to confirm the SI joint as the pain source.
Yes. Most patients improve with physical therapy, medications, and targeted injections.
SI joint pain usually stays above the knee and is centered in the lower back or buttock, while sciatica often radiates down the leg.
Minimally invasive surgery may be considered when conservative treatments fail and diagnostic injections confirm the SI joint as the pain source.

Toll Free: (855) 774-6334
Fax: (571) 208-0585
Conditions We Treat
Chronic Back Pain
Neck Pain
Arm Pain and/or Numbness
Leg Pain and/or Numbness
Herniated Disc – Lumbar and Cervical
Sacroiliac Joint (SI) Pain
Slipped Disc
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal Fractures
Whiplash Syndrome
Failed Back Surgery
Office Hours & Locations
Monday – Thursday: 8am – 4pm Friday: 8am – 2pm Loudoun County 24430 Stone Springs Blvd, Suite 250 Dulles, VA 20166 Spotsylvania County 4604 Spotsylvania Parkway, Suite 300 Fredericksburg, VA 22408 Prince William County 9625 Surveyor Ct. Suite 320 Manassas, VA 20110
